How Do Diesel Vehicles Work Using Biodiesel?
All diesel vehicles, whether classified as biodiesel or conventional diesel, are one and the same. They have the same internal combustion engine and components. Although all diesel vehicles can operate using biodiesel, some original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) do not approve the use of higher-level blends of biodiesel. Before using biodiesel, be sure to check your OEM engine warranty to ensure that higher-level blends of this alternative fuel are approved. The Engine Technology Forum provides a list of diesel vehicles with warranties covering blends above B5. Learn more about diesel vehicles using biodiesel.
High-res image
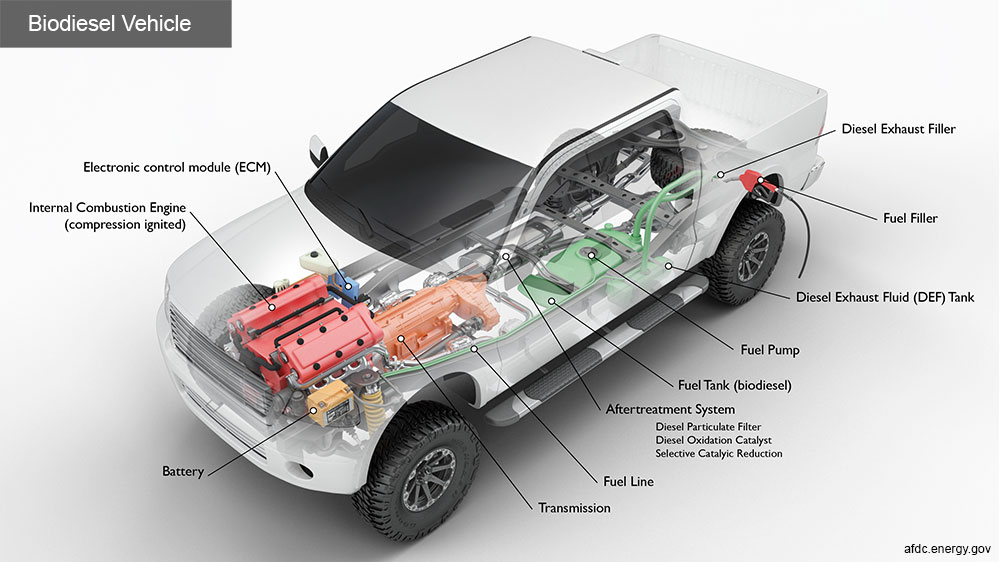
Key Components of a Biodiesel Vehicle
Aftertreatment system: This system is comprised of multiple components, which are responsible for filtering the engine exhaust gas to meet tailpipe emission requirements. After the exhaust gas of the engine is filtered through the diesel particulate filter (DPF) and the diesel oxidation catalyst to reduce particulate matter, diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) is injected into the exhaust gas mixture, then reduced to nitrogen and water by chemical conversion within the selective catalytic reducer (SCR) before being released into the atmosphere via the vehicle's tailpipe.
Battery: The battery provides electricity to start the engine and power vehicle electronics/accessories.
Diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) tank: This tank holds diesel exhaust fluid, an aqueous urea solution, which is injected into the exhaust stream during selective catalytic reduction.
Diesel exhaust fluid filler: This port is for filling the diesel exhaust fluid tank.
Electronic control module (ECM): The ECM controls the fuel mixture, ignition timing, and emissions system; monitors the operation of the vehicle; safeguards the engine from abuse; and detects and troubleshoots problems.
Fuel filler: A nozzle from a fuel dispenser attaches to the receptacle on the vehicle to fill the tank.
Fuel line: A metal tube or flexible hose (or a combination of these) transfers fuel from the tank to the engine's fuel injection system.
Fuel pump: A pump that transfers fuel from the tank to the engine's fuel injection system via the fuel line.
Fuel tank (biodiesel): A fuel tank stores fuel on board the vehicle until it's needed to power the engine.
Internal combustion engine (compression-ignited): In this configuration, fuel is injected into the combustion chamber and ignited by the high temperature achieved when a gas is greatly compressed.
Transmission: The transmission transfers mechanical power from the engine and/or electric traction motor to drive the wheels.