How Do Flexible Fuel Cars Work Using Ethanol?
Flexible fuel vehicles (FFVs) have an internal combustion engine and are capable of operating on gasoline and any blend of gasoline and ethanol up to 83%. FFVs have one fuel system, and most components are the same as those found in a conventional gasoline-only car. Some special ethanol-compatible components are required to compensate for the different chemical properties and energy content in ethanol, such as modifications to the fuel pump and fuel injection system. The engine control module (ECM) is also calibrated to accommodate the higher oxygen content of ethanol. Learn more about flex fuel vehicles.
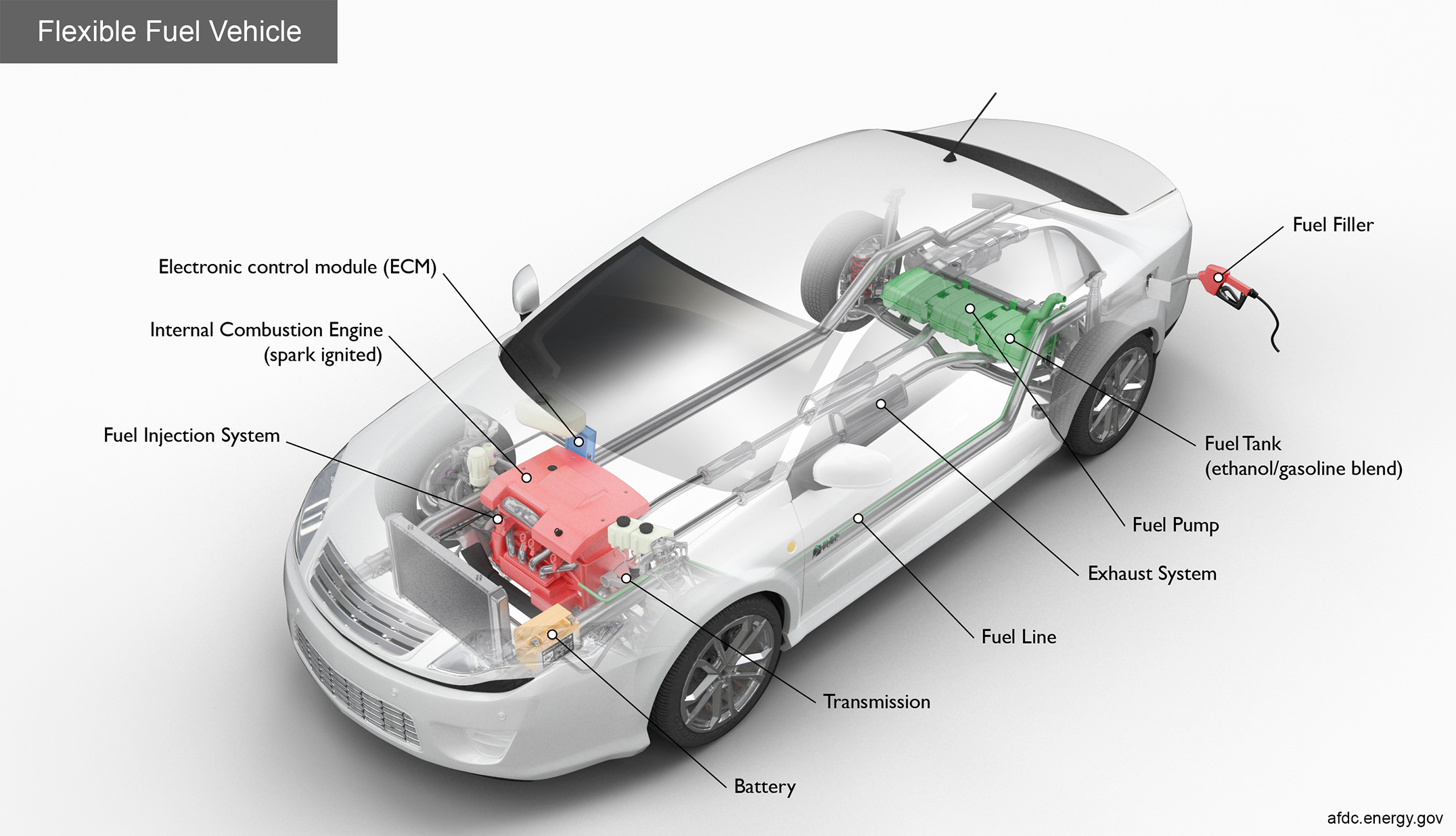
Key Components of a Flex Fuel Car
Battery: The battery provides electricity to start the engine and power vehicle electronics/accessories.
Electronic control module (ECM): The ECM controls the fuel mixture, ignition timing, and emissions system; monitors the operation of the vehicle; safeguards the engine from abuse; and detects and troubleshoots problems.
Exhaust system: The exhaust system channels the exhaust gases from the engine out through the tailpipe. A three-way catalyst is designed to reduce engine-out emissions within the exhaust system.
Fuel filler: A nozzle from a fuel dispenser attaches to the receptacle on the vehicle to fill the tank.
Fuel injection system: This system introduces fuel into the engine's combustion chambers for ignition.
Fuel line: A metal tube or flexible hose (or a combination of these) transfers fuel from the tank to the engine's fuel injection system.
Fuel pump: A pump that transfers fuel from the tank to the engine's fuel injection system via the fuel line.
Fuel tank (ethanol/gasoline blend): Stores fuel on board the vehicle to power the engine.
Internal combustion engine (spark-ignited): In this configuration, fuel is injected into either the intake manifold or the combustion chamber, where it is combined with air, and the air/fuel mixture is ignited by the spark from a spark plug.
Transmission: The transmission transfers mechanical power from the engine and/or electric traction motor to drive the wheels.